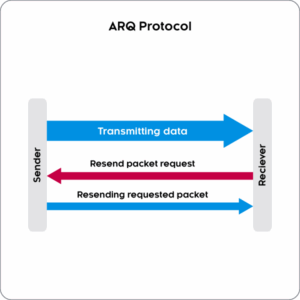
How Does the ARQ Protocol Work?
ARQ operates through a systematic error-detection and retransmission process:
- Error Detection – The receiver identifies corrupted or missing data packets using error-checking techniques like checksums.
- Acknowledgment (ACK/NACK) – If a packet is received correctly, the receiver sends an acknowledgment (ACK) to confirm delivery. If an error is detected, a negative acknowledgment (NACK) or silence prompts the sender to retransmit the data.
- Retransmission – The sender resends the requested packets until they are received correctly, ensuring data integrity even in unstable network environments.
This self-correcting mechanism makes ARQ essential for applications demanding high reliability and accuracy.
ARQ Protocol vs. Other Error Correction Technologies
ARQ vs. FEC (Forward Error Correction)
- ARQ: Detects and retransmits erroneous packets, optimizing bandwidth usage in networks with low to moderate packet loss.
- FEC: Adds redundant data to the original transmission, allowing the receiver to correct errors without retransmissions, making it ideal for high-latency or one-way communication channels.
ARQ vs. TCP/IP Reliability
- ARQ is a core component of protocols like TCP, enhancing data integrity through controlled retransmission.
- TCP/IP integrates ARQ with congestion control and flow management, ensuring seamless data delivery in various network conditions.
How Nevion Utilizes ARQ for IP Media Transport
Nevion leverages ARQ to ensure seamless, high-quality media transport over IP networks, particularly for:
- Live Broadcasts – Maintaining superior video and audio quality by mitigating packet loss.
- Remote Production – Enabling real-time collaboration with reliable media transport across distributed locations.
- IP Media Workflows – Providing a fault-tolerant transport layer for compressed and uncompressed media streams.
By integrating ARQ into its solutions, Nevion delivers exceptional performance in demanding broadcast and production environments.
Learn More