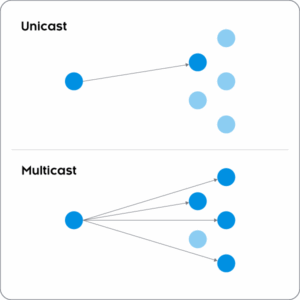
What is Unicast?
Unicast is a one-to-one communication model where data is transmitted from a single sender to a single receiver. This method is widely used for applications such as video streaming, web browsing, and VoIP. Each recipient receives an individual data stream, ensuring a personalized experience but consuming significant bandwidth when serving multiple users simultaneously.
Key Characteristics of Unicast:
- Direct one-to-one transmission
- High reliability and secure delivery
- Scalable for small-to-moderate audience sizes
- Bandwidth-intensive when scaling to multiple recipients
What is Multicast?
Multicast follows a one-to-many model, where a single data stream is transmitted to multiple recipients who have subscribed to receive it. This method is particularly efficient for applications like live broadcasting, IPTV, and real-time content distribution, as it reduces network congestion and optimizes bandwidth.
Key Characteristics of Multicast:
- Efficient one-to-many delivery model
- Reduces network load and bandwidth consumption
- Ideal for real-time video streaming and large-scale broadcasting
- Requires multicast-enabled network infrastructure and protocol support (e.g., IGMP, PIM-SM)
Which Transmission Method is Best?
The choice between unicast and multicast depends on the application (see the table below).
For dynamic media environments, multicast provides significant advantages, especially in minimizing redundant data transmission and ensuring synchronized content delivery.
How Nevion Utilizes Multicast
Nevion integrates multicast technology into its live production workflows, enabling:
- Scalable media transport with low-latency delivery
- Bandwidth-efficient video distribution across large networks
- Seamless synchronization of multiple feeds for broadcast applications
In high-demand environments, such as live sports and news production, multicast ensures high-quality, real-time content distribution without straining network resources.
Nevion: Pioneering Media Network Solutions
As a leader in IP-based media transport, Nevion delivers advanced solutions for content contribution, production, and distribution. By leveraging both unicast and multicast protocols, Nevion ensures seamless, high-performance media delivery for broadcasters, production studios, and media enterprises worldwide.
Why Choose Nevion?
- Industry-leading IP media transport solutions
- Scalable and secure network architectures
- Optimized multicast workflows for efficient content distribution
- Proven expertise in broadcast and live production environments
For more insights on optimizing media transport with Nevion’s multicast solutions, contact us today!